Will there ever be more services on the Freeview Light transmitters?
 Brian Butterworth published on UK Free TV
Brian Butterworth published on UK Free TV The digital terrestrial service that is known today as Freeview, started life in Parliament as the Broadcasting Act 1996.
Part I act gave the regulator, then the Independent Television Commission, the authority to establish digital terrestrial television services in the UK, and paved the way for a "six multiplex" service. One multiplex was reserved for the BBC, a second jointly between the "Channel 3 licence holder", Channel 4, Gaelic programming in Scotland plus Teletext UK as the "national teletext provider"
One half of the third multiplex was passed to Channel 5 and the S4C Corporation, with the remaining three and a half being put up for a public auction. The ITC duly awarded the remaining three multiplexes to "British Digital Broadcasting" in 1997, which was a combination of two big ITV companies at the time, Carlton and Granada.

On Sunday 15th November 1998, the services was launched under the name "ONdigital", a mixture of free-to-air and pay services, and rather dwarfed by the launch six weeks earlier of the much superior Sky Digital service.
ONdigital renamed itself ITVdigital on 11th July 2001, but the woollen monkey toy in the adverts proved more popular than the service, and the service closed on 1st May 2002.
 It became clear (especially to BBC director-general Greg Dyke, pictured right) that the digital terrestrial service was popular with viewers, but it was unsuitable as a pay-TV platform.
It became clear (especially to BBC director-general Greg Dyke, pictured right) that the digital terrestrial service was popular with viewers, but it was unsuitable as a pay-TV platform.
 ITVdigital handed back three multiplex licences to the ITC, and the ITC then re-awarded one to the BBC and the other two to Crown Castle International, a company formed when the BBC's engineering division was sold off.
ITVdigital handed back three multiplex licences to the ITC, and the ITC then re-awarded one to the BBC and the other two to Crown Castle International, a company formed when the BBC's engineering division was sold off.
A company, DTV Services, formed to publicise the new service, which was now called Freeview.
Sky joined in, and purchased slots on the new service (from CCI) for Sky News, Sky Sports News and Sky Travel. Also there from the start of Freeview was Flextech Television "ftn", music channel TMF, UKTV's UK History and UK Bright Ideas, and shopping channel, QVC
Digital switchover process
When it was decided that the analogue television signals would be turned off, the BBC, as it funded by a universal fee decided that it must provide the two multiplexes of services to all homes.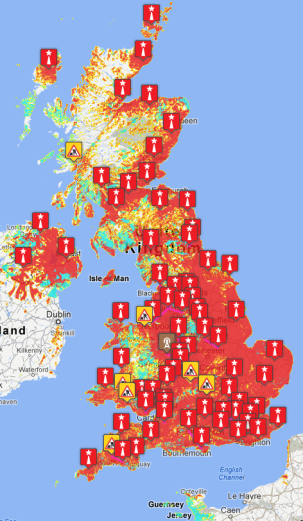 Ofcom, now the regulator, decreed that the multiplex shared by Channel 3 and Channel 4 (called "Digital 3 and 4 Ltd") must also provide service to all homes that had analogue. This was because Channel 4 already provided this level of coverage, and as the licence holder for Channel 3 has "public service obligations", the broadcasting of multiplex 2 should also extend to all existing TV masts.
Ofcom, now the regulator, decreed that the multiplex shared by Channel 3 and Channel 4 (called "Digital 3 and 4 Ltd") must also provide service to all homes that had analogue. This was because Channel 4 already provided this level of coverage, and as the licence holder for Channel 3 has "public service obligations", the broadcasting of multiplex 2 should also extend to all existing TV masts.
However, for the commercial multiplexes, Ofcom simply invited Crown Castle Ltd and S4C Digital Networks (SDN) to apply to extend their networks. Ofcom, having granted the multiplex licences already, felt it had no legal power of compulsion to insist more homes were served, and in December 2006 announced that no application had been received - at this point Ofcom no longer planned for additional frequencies for the commercial multiplexes.
Both commercial operators decided that the cost of providing the equipment, installation and ongoing operation of services from the 1,000 smaller transmitters would cost more than any additional revenue they could get from the TV channels that rent their broadcast capacity, as the work would only expand the actual number of homes broadcast to by 9%.
Since this time, S4C Digital Networks multiplex was bought by ITV plc, and Arqiva acquired the CCI multiplexes. For this reason the commercial multiplexes are known as SDN, ArqA and ArqB.
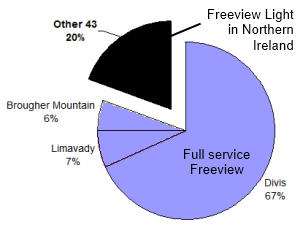 The map shows the locations where Freeview Light service is generally the only Freeview reception option.
The map shows the locations where Freeview Light service is generally the only Freeview reception option.
See also: Where are the public service (Freeview Light) transmitters?
9:10 PM
Ade Langford:
Hi there. Noted, thanks for the update.
| link to this comment |