2 days left of analogue television - goodbye teletext
 Brian Butterworth published on UK Free TV
Brian Butterworth published on UK Free TV This is ORACLE
Information at your fingertips...Television and radio provide up-to-the-minute news and information; but, for many purposes, the written word is more useful. Written material has the advantage that it can be read at any pace, the reader can stop to think, perhaps re-read the text a number of times.

ORACLE retains the power of presenting the most immediate news and information possible, yet combines it with the advantages of written material. Information is transmitted alongside the television picture, and an ORACLE receiver extracts and displays it in the form of characters and symbols on the television screen. An extra set of controls at the receiver allows the selection of any one of up to 800 different pages. At any time the viewer can choose to watch either the normal television programme or the ORACLE pages or even, on some receivers, the ORACLE pages superimposed upon the programme.
The pages can contain anything that appeals to the viewing public. At the moment ORACLE offers an extensive range of the news and information that we need or are interested in, every day.
Choosing a page is even easier than dialling a telephone number and the cost of an ORACLE receiver will be within reach of very many viewers.
The ORACLE service
ORACLE uses the broadcast television signal to carry extra information. These extra signals do not interfere with the transmission and reception of normal programmes. An ORACLE receiver - a television receiver with additional circuits - is capable of reconstructing written information and displaying it on the screen. 'Me system allows the transmission of very many bulletins of information, and the viewer can choose any one by selecting a three-figure number on a set of controls - usually push buttons or thumbwheel switches. After short interval the information appears and remains for as long as it is needed.A major use of ORACLE is as an information service, but it can also supplement normal television programmes with sub-titles or linked pages.
The entire signal is accommodated within the existing 625-line television allocation, and so costs nothing in terms of radio frequency spectrum space. It is, effectively, the first broadcasting system to transmit information in digital form.
How did ORACLE come about?
ORACLE was initially the product of a team of IBA engineers. The name is an acronym for Optional Reception of Announcements by Coded Line Electronics. A service with information generated by computer was demonstrated first by the IBA early in 1973. Later, the organisations with an interest in such systems came together, with the object of devising a unified standard. A specification for the resulting system was first published in 1974 but was later revised and issued in September 1976 (ref. 1). The generic title 'Teletext' is now often used, but the name ORACLE remains for ITV's service.The first ORACLE system allowed up to 50 pages, with text in only one colour. Although the technical basis is similar, the current system is snore attractive and flexible - with many more pages, colours, and other features. This new system is the result of co-operation and the pooling of ideas by UK Broadcasters and Receiver Manufacturers.
In 1974 the Home Office authorised a trial period for experimental Teletext services and this period was extended in Autumn 1976. The rev programme companies have been providing an experimental service since mid-1975.
What do ORACLE pages look like?
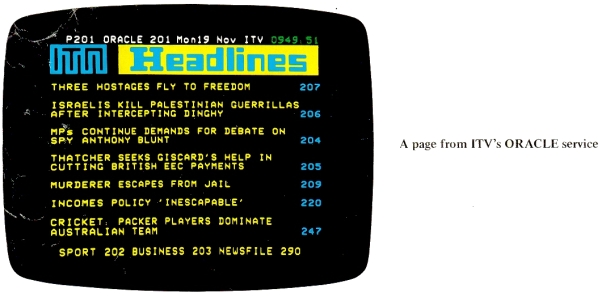
ORACLE pages look rather like pages of typescript, except that they can also include large-sized letters and simple drawings. The photographs in this leaflet show a few examples.The standard-sized words (like those in the central paragraph on the 'Consult the ORACLE' page) can use upper or lower case, and be in any one of six colours - red, green, blue, yellow, cyan and magenta - or white. The shape of the characters is usually based on a 7 x 5 dot matrix, with a refinement known as character rounding.
As many as 24 rows of the standard-sized characters can be fitted on a page, and each row can have up to 40 characters. Each page can carry about 150-zoo words (about 3 paragraphs on this page).
The specification also allows the option of characters of twice the height of standard characters.
Larger-sized characters and also drawings are made by assembling small illuminated rectangles, each one-sixth the size of the space occupied by a standard character, and these too can be in any of the six colours or in white.
The row at the top of the screen always has the same format. It contains the title ORACLE, the page number or a cycling page number (or both), the day and he date, an ITV identification and the time, exact to the nearest second.
The remaining 23 rows can be made up of rows or part rows of text or the 'graphic' forming rectangles.
Part or all of each page can be made to flash on-and-off (usually once per second), to emphasise any particular item.
The page background is usually black, although the specification allows the editor to define different back-ground colours for part or all of the screen. Also, at the ORACLE editor's discretion, text can be enclosed in a black window and cut into the normal picture. Further, certain receiver designs allow the whole page (sometimes in white only) to be superimposed upon the picture.
It is potentially possible for the system to carry up to Boo single pages; but because of the way the pages are transmitted, this could mean an appreciable waiting time between page selections. So for the moment not all 800 pages are used at any one time.
Making more ORACLE pages available
The number of different pages available can be extended in two special ways:1. By MULTI-PAGES or self-changing pages. Here the content of the page is altered after allowing sufficient time for it to have been read. The new pages appear automatically. They could contain, for example, lists of sports results - say, one League Division per page.
2 By TIME-CODED PAGES or transmission-time addressed pages. All pages can be addressed (or labelled) not only by their number but also x;., the time at which they are transmitted. Usually the transmission time (or time-code) label is not used by the ORACLE receiver, but it can be set to select both page number and time. If it is, then different pages can be transmitted on the same page number at different times of the day. This still allows the viewer to choose which page he sees, provided he knows and pre-sets its transmission time.
The ORACLE data is added to the normal television signal, and the combined signal is transmitted. Pages are chosen on an ORACLE receiver merely by selecting a three-figure number.
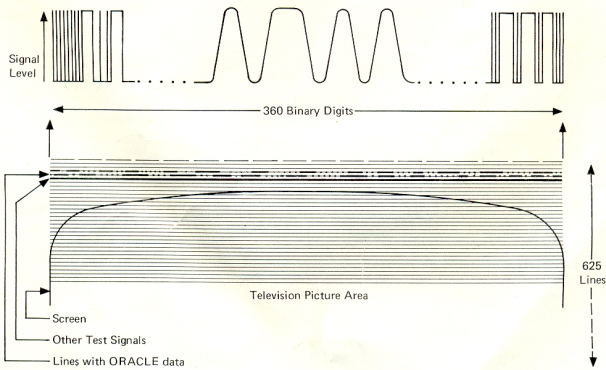
How is ORACLE transmitted?
Television picture transmissions are made up of a large number of horizontal lines, but not all the lines are used to form the picture. About 40 or so lines are arranged to be off the top of the screen - like a horizontal border at the top of a photograph. Into this border we put our ORACLE information.A television picture is made up by interlacing two sets of 312 1/2 lines, 25 times a second. Into the 17th and 18th lines of each of these two sets (in the second set they are called 330 and 331) the ORACLE information is inserted in the form of binary pulses. If the height control on a receiver is incorrectly adjusted it is possible to see these as lines of bright dots above the picture.
Each line of pulses contains the coded data for one row of standard size text or graphics rectangles. The rows for a given page are transmitted one after another until the page is complete, then the next page and so on, until all the pages have been transmitted. Then the cycle begins again. It's like a conveyer belt system, with coded rows of text continuously loaded on, one after another.
If every line of a page has text or graphics on it, the page takes 0.24 seconds to transmit. The total time to transmit the complete cycle of pages depends on how many pages there are, and how full they are. This cycle time represents the maximum waiting time for the appearance of a page after selection.
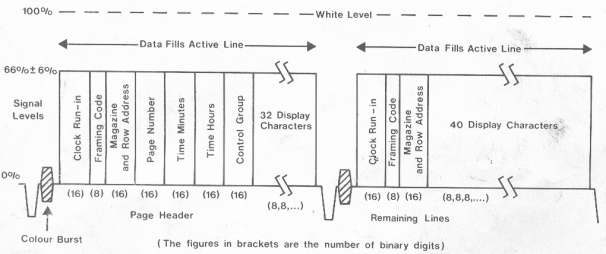
The binary pulses on the data lines are grouped into two sections. The first section establishes which row of text it is on the page, and the second defines what is to make up the row. Each letter, number, or graphic symbol is represented by an eight-digit binary number. For the first row of the page the first section also establishes which page is coming up, and its 'time-code'.
What is needed to receive ORACLE
Additional circuits are needed in a television receiver to decode ORACLE. First, data extraction and recognition circuits examine the incoming 'conveyer belt' of ORACLE data lines, and extract those signals which make up the page which has been selected. The data from these lines is then stored (usually in an integrated circuit called a 'Random Access Memory') so that the page can be displayed at the same rate as a normal picture. The binary number codes are then translated to their corresponding characters or graphics patterns (in a 'Read Only Memory'). Finally a video raster scan representation of the page is switched onto the screen. The reception of ORACLE, like normal television, is susceptible to various kinds of interference. IBA trials, however, indicate that the great majority of those who receive television pictures well, will also be able to receive ORACLE.How is ORACLE generated?
Independent Television staff at special ORACLE editorial suites usc small computers to convert their copy to the sequences of pulses needed for transmission. These are then added to the normal television signal and the combined signal is transmitted.The staff gather news and facts from a wide range of sources. Direct links to news agencies, etc. provide an up-to-the-minute service which can be conveyed to ORACLE within seconds.
ORACLE the future
At the moment ORACLE provides a news and information service, and Independent Television is considering ways of extending the service. The ORACLE text can be super-imposed on the normal picture, so sub-titles or notes can be used to supplement programmes. Particular interest is being shown in educational uses of this.ORACLE signals originated in London are broadcast in other regions when the local ITV company uses programmes from London. When a programme company is using programmes originating outside London, usually locally, the data from London can be added by using a unit designed by ITV engineers and known as a data bridge. Data bridges are now installed in nearly all ITV regions and it is anticipated that, eventually, the ORACLE service will contain information generated in the local ITV region itself.
Interest in the current ORACLE development period, and the continuing work on ideas for extending the service, point to a very exciting future for ITV'S ORACLE.
ORACLE brief specification

Help with Freeview, aerials?
In this section
Monday, 22 October 2012
T
trevorjharris10:17 AM
Actually it was not only teletext that was transmitted in this way. It was also used commercially for data broadcasting. This was used by betting shops to receive racing information. One betting shop used a system called Naplps which was a more advanced videotext system. It could also control the televisions in the shop.
| link to this comment |
trevorjharris: as well as 4Tel on channel 4 and telesoftware on Ceefax.
All those hidden pages with hexadecimal digits A to F in them...
| link to this comment |
B
Bill12:04 PM
I spent many a happy day decoding these hidden pages, on my 4Tel Volex (I think it was called Volex - It's in my loft) Teletext adapter on my Sinclair ZX Spectrum. They contained may BBC Micro programs. Unfortuantely, only one program was ever transmitted for the ZX Spectrum.
| link to this comment |
J
John Robinson2:59 PM
Edinburgh
I remember Ceefax well. I had some of my software published by the Telesoftware service, and I have a Telesoftware polo shirt somewhere. It's too small now though.
| link to this comment |
John's: mapJ's Freeview map terrainJ's terrain plot wavesJ's frequency data J's Freeview Detailed Coverage
It's also interesting to note that there are 360 bits per line in the teletext broadcast.
Which is, of course, half of the 720 samples per line in the "main profile at main level" in MPEG-2 for "625-line television", or 576i.
This (sort of) equates to a "forward error correction" of 1/2.
Only 576 lines of the 625 lines are used for the picture, which is why other 49 could be used for teletext services.
Note also that teletext is in "in band" service, carried as part of the picture, and not an "out band" service like NICAM which is carried on a different carrier.
| link to this comment |
Another interesting feature of the "fast text" service that uses the coloured buttons in teletext is the use of Hamming Coding - Hamming(7,4) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia .
| link to this comment |
Mark A.
6:34 PM
6:34 PM
I have a video of the last Ceefax testcard shown on BBC Two digital this morning.
See The last few seconds of the last ever Ceefax testcard. - YouTube
The top line sad
152 CEEFAX 1 152 Mon 22 Oct ....
as used on BBC1 and not
152 CEEFAX 2 152 Mon 22 Oct ....
The page number was replaced with 010 ten minutes before the end, then 005, 003 and 001 as a countdown to the end.
The display used to display Teletext characters is the BBC Micro screen Mode 7.
This screen mode uses less memory than other screen modes, as each character is treated as a pixel.
The characters 0 to 255 are used to display a character, select a character colour or graphic colour.
See MODE 7 - BeebWiki
| link to this comment |
Mark A.: Actually, you're not quite right about BBC Mode 7.
In teletext mode, each character is a character not a pixel. The pixels were generated from the ROM, so each of the 40x24 lines used a byte.
In teletext mode, the colour was changed using a character, and there were codes such as "switch to graphics colour", where each of the following characters represented a six bit graphic (2 horizontal, 3 vertical) with some characters remaining normal.
The top bit wasn't used in normal teletext systems (as it was used for "parity").
As the colour and other codes were bytes, they occupied a space on the screen (unlike the way VT-100 works, for example).
One difference between Mode 7 and normal teletext was that you had to repeat the characters of double height text.
The ZX Spectrum had a mono-bitmap screen, by comparison, but with foreground and background colours set for every 8x8 pixels.
The BBC other modes were bitmapped and palette mapped.
| link to this comment |
Select more comments
Your comment please!